What is Drilling?

Drilling is a process of creating holes in a solid material such as rock, wood, or metal. This is done by using a tool called a drill, which has a sharp pointy end called a bit that rotates at high speed, cutting into the material and creating a hole. Drill bits come in a variety of shapes and sizes like Twist drill bits, Brad-point bits, Spade bits, Forstner bits, etc. the best type of bits to use depend on the situation as they all have their specific advantages and disadvantages. Drilling is a widely used technique in many industries, such as construction, mining, oil and gas, manufacturing, and more. The size and shape of the hole can vary depending on the type of material and the purpose of the drilling. Drilling is an essential process in creating everything from buildings to pipelines to electronic devices.
Origins of Drilling

Drilling is an essential process that has been used for thousands of years, starting from ancient times to the modern era. The earliest form of drilling can be traced back to ancient Egypt, where the Egyptians used what can be very likely assumed to be copper drills to bore holes in stones and rocks. The ancient Romans also used drilling techniques to extract salt and minerals from the earth by using what is known as auger drills. The Chinese were known to incorporate bamboo in their drilling activities such as by using them as pipelines or by combing the iron drill bits they created with some bamboo parts.
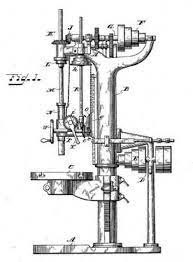
During the Middle Ages, drilling technology was not advanced, and simple hand tools were used to drill wells. It wasn’t until the 17th century that the first mechanical drilling machines were invented. These early drilling machines used steam engines and were mainly used for drilling water wells.
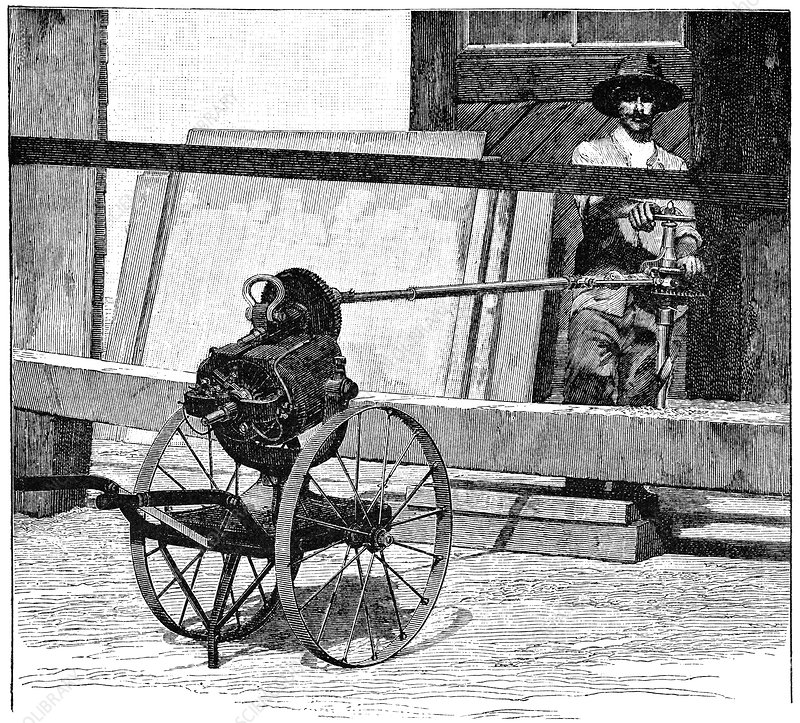

In the 19th century, the introduction of electricity led to the development of electric drilling machines, which revolutionized the mining industry. Electric drills were more efficient, faster, and reliable than steam-powered ones.
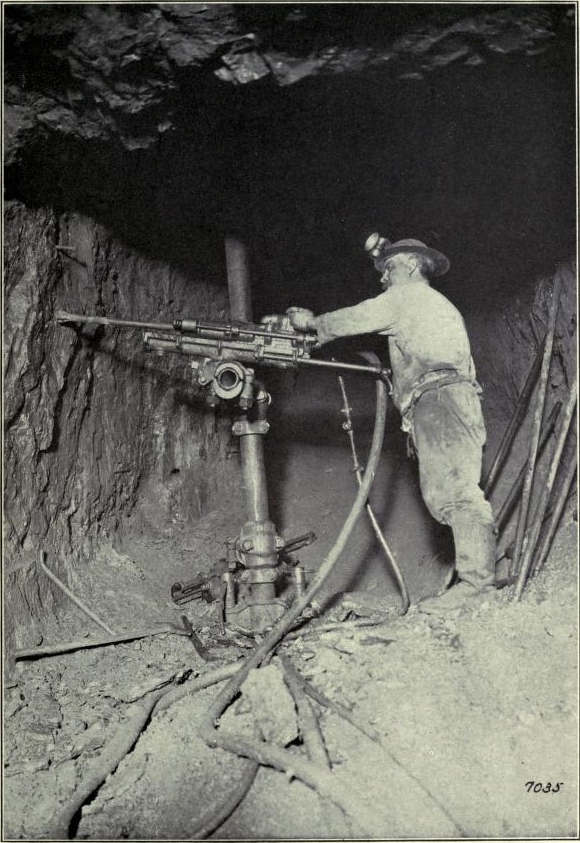

The 20th century saw significant advancements in drilling technology, with the development of hydraulic drilling machines and the use of high-pressure water jets for drilling. These innovations allowed for faster drilling and the ability to drill deeper into the earth.

Today, drilling technology continues to evolve, with the development of advanced computer-controlled drilling machines and the use of lasers for drilling. These modern drilling techniques have significantly increased drilling speed, accuracy, and safety.

Fun fact: The world’s largest drill, known as the Big Bertha, was used to drill a tunnel for a highway in Seattle, Washington. The drill was 57 feet in diameter and weighed 6,700 tons. It was so massive that it had to be assembled on-site and could only be moved at night to avoid disrupting traffic.
Future of LPG in Drilling

Liquefied Petroleum Gas (LPG) is a clean-burning and versatile fuel that has been used in various applications, including drilling. Over the years, the use of LPG in drilling has increased due to its efficiency, cost-effectiveness, and environmental benefits. In recent years, most industries including the drilling industry have been shifting towards using more environmentally friendly fuels due to climate change concerns, and LPG is emerging as a promising alternative to traditional fossil fuels like diesel and gasoline.
One of the main advantages of using LPG in drilling is its lower emissions profile compared to diesel or gasoline. LPG produces significantly lower levels of harmful emissions such as carbon monoxide, nitrogen oxides, and particulate matter. This makes LPG a more environmentally friendly option for drilling operations, particularly in areas where air quality is a concern.
Another advantage of using LPG in drilling is its high energy content. LPG has a higher energy content per unit volume than diesel or gasoline, meaning less fuel is needed to generate the same amount of energy. This translates into lower fuel costs and increased efficiency for drilling operations.
In addition to its environmental and cost benefits, LPG is also a safer fuel option for drilling operations. Unlike diesel or gasoline, LPG is non-toxic and non-carcinogenic. It also has a lower risk of fire and explosion due to its high ignition temperature.
The market trends for LPG in drilling are also positive. According to a report by Grand View Research, The global liquefied petroleum gas market size was estimated at USD 117.3 billion in 2022 and is expected to expand at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 3.7% from 2023 to 2030. This growth is attributed to the increasing demand for LPG in various end-use industries, including drilling.
Moreover, many drilling companies have already made the switch to LPG as a fuel source. For example, Atlas Copco, a leading provider of drilling equipment, has developed a range of LPG-powered drilling rigs that offer several benefits, including lower emissions and improved fuel efficiency.
In conclusion, LPG is emerging as a promising fuel source for drilling operations. Its lower emissions, higher energy content, and safety benefits make it an attractive alternative to traditional fossil fuels like diesel and gasoline. Additionally, the positive market trends and increasing adoption by drilling companies suggest a bright future for LPG in the drilling industry.