What is sterilization?

Sterilization is an extremely important process used to eliminate microorganisms from a surface or substance. This process is incredibly important in various industries, such as healthcare and the food industry, where the spread of bacteria and other microorganisms can cause various illnesses and diseases like Hepatitis B, Hepatitis C, HIV or AIDS, MRSA, Tuberculosis, etc. Essentially, sterilization is the act of ensuring that a surface or substance is completely clean and free from any harmful organisms that could cause harm to humans or animals.
It’s important to note that sterilization is different from disinfection, which is the process of reducing the number of microorganisms on a surface or substance that is not necessarily completely removing them. While disinfection can help to reduce the spread of bacteria and viruses, sterilization is necessary in situations where a completely clean environment is needed, such as in surgical settings.
Origins of Sterilization

In ancient times, people relied on basic methods to sterilize objects and surfaces. One common method was boiling water, which was effective in killing bacteria and other microorganisms. Additionally, exposing objects to sunlight was also a popular method of sterilization. The ancient Egyptians, for example, used hot sand to prevent infections in wounds.
As time progressed, sterilization techniques became more advanced. In the 19th century, scientists began to experiment with disinfectants such as carbolic acid, which could kill bacteria on various surfaces. However, these early disinfectants were often toxic and dangerous to use and so were discontinued after a brief period of experimentation with them.

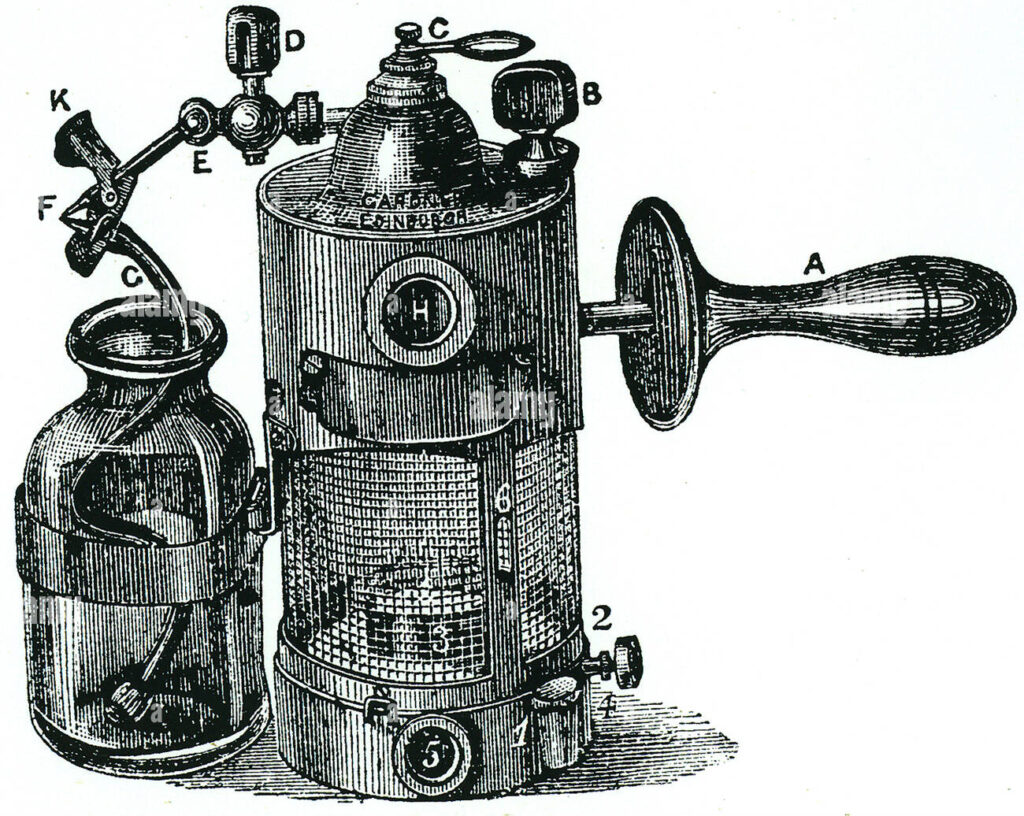
The development of the autoclave in the late 19th century was a major breakthrough in sterilization technology. An autoclave is a device that uses high pressure and steam to kill bacteria and other microorganisms on equipment and surfaces. This type of technology is still widely used (obviously it has advanced significantly) in medical and laboratory settings today.

In the 20th century, sterilization techniques continued to evolve. The discovery of antibiotics in the 1920s and 1930s revolutionized medicine and made it possible to treat infections that were once deadly. However, overuse of antibiotics has led to the development of antibiotic-resistant bacteria like Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA), Vancomycin-resistant Enterococcus (VRE), etc. making sterilization more important than ever.
Today, a variety of sterilization techniques are used in healthcare settings, laboratories, and food production facilities. These techniques include steam sterilization, chemical sterilization, and radiation sterilization. Each technique has its own advantages and disadvantages, and the choice of technique depends on the specific application level of sterilization required.
How is LPG useful for sterilization?
LPG (Liquefied Petroleum Gas) is a clean-burning fuel that is commonly used in modern sterilization techniques. The use of LPG in sterilization is a safe and efficient way to remove harmful bacteria and viruses from surfaces and equipment. This is so because LPG is a readily available fuel that can be easily transported and stored in tanks as it can also be converted into a liquid and stored like that due to its low boiling temperature. This low boiling point also allows the LPG to easily vaporize and ignite, providing a reliable and efficient source of heat even in colder climates such as Norwegian countries like Sweden and Finland(Winters can go as low as -22 Celsius).

One modern sterilization technique that uses LPG is called the Sterilwave system. This system is used in healthcare facilities and laboratories to sterilize biomedical waste, such as used medical equipment and contaminated dressings. The Sterilwave system works by using a shredder to break down biomedical waste into smaller pieces. The waste is then loaded into a sterilization chamber, where it is exposed to steam from a steam generator. LPG is used as the energy source for the sterilization process for the various machines involved in the entire process, and its clean-burning properties make it an environmentally friendly choice.
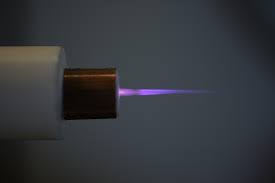
Another popular sterilization technique that uses LPG is called low-temperature plasma sterilization. This technique is commonly used in the medical industry to sterilize delicate equipment that cannot withstand high temperatures. Gases like argon and oxygen, as well as mixtures of air and hydrogen, nitrogen, are used for generating plasma. is used to generate plasma, which is a gas that contains charged particles. These charged particles destroy microorganisms by breaking down their cell walls. The low-temperature plasma sterilization process is gentle and effective, making it an ideal choice for sterilizing delicate equipment.

LPG is also used in sterilization techniques that involve the use of dry heat. In these techniques, LPG is again used as the energy source to generate high temperatures that destroy all microorganisms present on surfaces and equipment (the microorganisms are oxidized due to this high temperature). Dry heat sterilization is commonly used in the pharmaceutical industry to sterilize equipment and surfaces that cannot be sterilized using other methods.
Conclusion
In conclusion, sterilization is an essential process for maintaining public health and safety by eliminating harmful microorganisms from medical equipment, laboratory tools, and other surfaces. Proper sterilization techniques can prevent the spread of infectious diseases and ensure that medical procedures are conducted safely and effectively.
LPG (liquefied petroleum gas) plays a role in sterilization as a fuel source for certain types of sterilization equipment, such as autoclaves, plasma sterilization, dry heat sterilization, steriliwave etc. Autoclaves are commonly used in medical and laboratory settings to sterilize equipment and materials using high-pressure steam. LPG is often used as the fuel source for the boilers that generate the steam used in the autoclave.
However, it’s important to note that not all sterilization methods use LPG, and many modern sterilization technologies, such as Sterilwave can use alternative energy sources to sterilize medical waste such as electricity, natural gas etc. These new technologies are more sustainable, cost-effective, and environmentally friendly, making them a promising alternative to traditional sterilization methods.